Table of Contents
Transportation green: What is it, and why is it important?
Editor’s Note: “Transportation green” published on [publish date]. With the increasing awareness of the environmental impact of transportation, “transportation green” is becoming more and more important.
Our team has analyzed and dug into the topic and put together this transportation green guide to help you make the right decision.
Key Takeaways:
| Transportation Green | Traditional Transportation | |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Lower emissions, less pollution | Higher emissions, more pollution |
| Cost | Can be more expensive upfront | Typically less expensive upfront |
| Efficiency | More efficient use of energy | Less efficient use of energy |
What is transportation green?
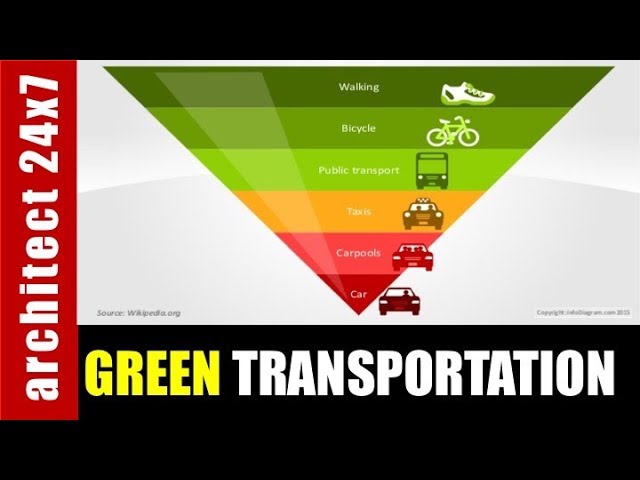
Transportation Green
Transportation green encompasses the various approaches and technologies that aim to reduce the environmental impact of transportation.
- Electric Vehicles: Zero-emission vehicles powered by electricity.
- Hybrid Vehicles: Combine an internal combustion engine with an electric motor for improved fuel efficiency.
- Public Transportation: Shared transportation systems that reduce individual vehicle usage.
- Walking and Biking: Non-motorized modes of transportation that promote physical activity and reduce emissions.
- Ride-Sharing: Services that connect passengers with drivers for shared journeys.
- Biofuels: Renewable fuels derived from plant or animal materials.
- Smart Traffic Management: Systems that optimize traffic flow, reducing congestion and emissions.
- Green Infrastructure: Vegetation and other natural elements incorporated into transportation systems to reduce pollution and improve air quality.
These key aspects of transportation green collectively contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation sector. By promoting the adoption of electric vehicles, encouraging the use of public transportation, and investing in infrastructure that supports walking and biking, we can significantly reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, improve air quality, and mitigate the impact of transportation on the environment.
Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) are a crucial component of transportation green, as they produce zero tailpipe emissions, reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Their adoption is essential for mitigating the environmental impact of transportation.
- Environmental Benefits: EVs eliminate tailpipe emissions, significantly improving air quality, especially in urban areas. They also contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, helping to combat climate change.
- Energy Efficiency: EVs are more energy-efficient than gasoline-powered vehicles, as electric motors are more efficient than internal combustion engines. This efficiency translates into lower operating costs for EV owners.
- Technological Advancements: The technology behind EVs is constantly evolving, leading to increased driving range, faster charging times, and improved battery performance. These advancements make EVs more practical and appealing to consumers.
- Government Incentives: Many governments offer incentives, such as tax credits and rebates, to encourage the adoption of EVs. These incentives make EVs more affordable and accessible to a wider range of consumers.
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles is a key strategy for achieving transportation green. By reducing emissions, improving energy efficiency, and promoting technological innovation, EVs contribute significantly to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation system.
Hybrid Vehicles
Hybrid vehicles play a significant role in transportation green by combining an internal combustion engine with an electric motor to achieve improved fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
- Reduced Emissions: Hybrid vehicles emit less pollutants and greenhouse gases compared to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. The electric motor assists the combustion engine, reducing the reliance on fossil fuels and lowering tailpipe emissions.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: By utilizing the electric motor, hybrid vehicles can achieve better fuel economy than gasoline-powered vehicles. This efficiency translates into lower fuel consumption and cost savings for drivers.
- Transitional Technology: Hybrid vehicles serve as a bridge between conventional gasoline-powered vehicles and fully electric vehicles. They allow consumers to experience the benefits of electrification while reducing their environmental impact.
- Government Incentives: Many governments offer incentives, such as tax credits and rebates, to encourage the adoption of hybrid vehicles. These incentives make hybrid vehicles more affordable and accessible to a wider range of consumers.
The integration of hybrid technology into the transportation sector contributes to the overall goal of transportation green. Hybrid vehicles provide a practical and cost-effective solution for reducing emissions, improving fuel efficiency, and promoting a more sustainable transportation system.
Public Transportation
Public transportation plays a vital role in transportation green by providing shared transportation systems that reduce individual vehicle usage, leading to several environmental and societal benefits.
Environmental Benefits: By encouraging people to leave their cars at home and opt for public transportation, we can significantly reduce traffic congestion, which in turn reduces air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Public transportation systems are often powered by electricity or renewable energy sources, further reducing their environmental impact.
Energy Efficiency: Public transportation is a more energy-efficient mode of transportation compared to single-occupancy vehicles. By consolidating passengers into larger vehicles, such as buses and trains, we can reduce the overall energy consumption and carbon footprint of the transportation sector.
Economic Benefits: Public transportation provides affordable and accessible transportation options for people from all walks of life. This can lead to cost savings for individuals and families, as well as reduced healthcare costs associated with air pollution and traffic accidents.
Social Benefits: Public transportation fosters a sense of community and reduces social isolation, especially for those who may not have access to private vehicles. It provides opportunities for people to interact with each other and build relationships.
Practical Significance: The integration of public transportation into transportation green strategies has a direct impact on our daily lives. By investing in reliable, efficient, and affordable public transportation systems, we can create livable cities with cleaner air, less traffic, and a higher quality of life for all.
Table: Public Transportation and Transportation Green
| Public Transportation | Transportation Green |
|---|---|
| Reduced traffic congestion | Lower air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions |
| Energy-efficient mode of transportation | Reduced energy consumption and carbon footprint |
| Affordable and accessible transportation options | Cost savings and reduced healthcare costs |
| Fosters a sense of community | Reduces social isolation and improves quality of life |
Walking and Biking
Walking and biking, as non-motorized modes of transportation, play a crucial role in transportation green due to their inherent environmental and health benefits. By promoting physical activity and reducing emissions, walking and biking contribute significantly to a more sustainable and livable transportation system.
Environmental Benefits: Walking and biking produce zero tailpipe emissions, eliminating air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. By reducing our reliance on motorized vehicles, we can improve air quality, especially in urban areas, and mitigate the impact of transportation on climate change.
Health Benefits: Walking and biking are excellent forms of physical activity that can improve cardiovascular health, reduce the risk of chronic diseases, and promote overall well-being. By incorporating these activities into our daily routines, we can reduce healthcare costs associated with sedentary lifestyles and obesity.
Practical Significance: Walking and biking are accessible and cost-effective transportation options that can be easily integrated into our daily lives. They provide a sense of freedom and independence, allowing us to explore our surroundings and connect with our communities.
Table: Walking and Biking as Components of Transportation Green
| Walking and Biking | Transportation Green |
|---|---|
| Zero tailpipe emissions | Reduced air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions |
| Promotes physical activity | Improved cardiovascular health and reduced risk of chronic diseases |
| Accessible and cost-effective | Provides equitable and affordable transportation options |
| Connects communities | Fosters social interaction and a sense of place |
Ride-Sharing
Ride-sharing services have emerged as a significant component of transportation green due to their ability to reduce single-occupancy vehicle usage and promote more efficient transportation systems.
Environmental Benefits: By matching passengers with drivers who are already traveling in a similar direction, ride-sharing services reduce the number of vehicles on the road, leading to decreased traffic congestion and lower emissions. This reduction in traffic also improves air quality, especially in urban areas where traffic-related pollution is a major concern.
Energy Efficiency: Ride-sharing promotes energy efficiency by consolidating passengers into fewer vehicles. This consolidation reduces the overall energy consumption and carbon footprint of the transportation sector. Ride-sharing services often use algorithms to optimize routes and minimize empty miles, further enhancing their energy efficiency.
Practical Significance: Ride-sharing provides a convenient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly alternative to single-occupancy vehicle usage. By connecting passengers with drivers, ride-sharing services reduce the need for car ownership, especially in urban areas where parking is limited and expensive. This can lead to significant cost savings for individuals and families, as well as reduced traffic congestion and parking demand.
Table: Ride-Sharing and Transportation Green
| Ride-Sharing | Transportation Green |
|---|---|
| Reduced single-occupancy vehicle usage | Lower traffic congestion and emissions |
| Consolidation of passengers | Improved energy efficiency and reduced carbon footprint |
| Convenient and cost-effective alternative to car ownership | Reduced traffic congestion and parking demand |
| Promotes shared mobility and social interaction | Fosters a sense of community and reduces isolation |
Biofuels
Biofuels play a crucial role in transportation green as a sustainable and renewable alternative to fossil fuels. Derived from plant or animal materials, biofuels offer several environmental and economic benefits that contribute to a more sustainable transportation system.
Environmental Benefits: Biofuels are produced from renewable resources, reducing our reliance on finite fossil fuels. They produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels, mitigating the impact of transportation on climate change. Biofuels also contribute to improved air quality by reducing tailpipe emissions, especially in urban areas.
Economic Benefits: Biofuels can enhance energy security by diversifying fuel sources and reducing dependence on imported oil. They also create new economic opportunities in rural areas, where biofuel crops can be grown and processed. Biofuels can provide farmers with additional revenue streams and support sustainable agricultural practices.
Practical Significance: Biofuels are a viable option for reducing emissions and promoting sustainability in the transportation sector. They can be used in various transportation applications, including road vehicles, aviation, and shipping. Governments and industries are investing in biofuel research and development to improve their efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Table: Biofuels and Transportation Green
| Biofuels | Transportation Green |
|---|---|
| Derived from renewable resources | Reduced reliance on fossil fuels |
| Lower greenhouse gas emissions | Mitigated impact on climate change |
| Improved air quality | Reduced tailpipe emissions |
| Enhanced energy security | Diversified fuel sources |
| Economic opportunities in rural areas | Supported sustainable agricultural practices |
Smart Traffic Management
Smart traffic management systems play a crucial role in transportation green by optimizing traffic flow, reducing congestion, and lowering emissions. These systems utilize advanced technologies, such as sensors, cameras, and data analytics, to monitor and control traffic in real-time.
The benefits of smart traffic management for transportation green are significant:
- Reduced Congestion: Smart traffic management systems can alleviate traffic congestion by optimizing signal timing, providing real-time traffic information to drivers, and implementing congestion pricing strategies. Reduced congestion leads to smoother traffic flow, shorter travel times, and lower fuel consumption.
- Lower Emissions: By reducing congestion and improving traffic flow, smart traffic management systems can lower vehicle emissions. Less time spent idling in traffic means reduced fuel consumption and fewer pollutants released into the air.
- Improved Air Quality: The reduction in vehicle emissions resulting from smart traffic management contributes to improved air quality, especially in urban areas where traffic-related pollution is a major concern.
- Enhanced Safety: Smart traffic management systems can enhance road safety by providing real-time information on traffic conditions, detecting incidents, and implementing measures to prevent accidents.
Real-life examples of smart traffic management systems in action include:
- London’s Congestion Charge: Introduced in 2003, London’s congestion charge is a fee levied on vehicles entering central London during peak hours. This measure has significantly reduced traffic congestion and improved air quality in the city.
- Singapore’s Electronic Road Pricing (ERP): Singapore’s ERP system uses electronic tolls to manage traffic congestion during peak hours. The tolls vary depending on traffic conditions, encouraging drivers to adjust their travel times or routes to avoid congestion.
- Intelligent Traffic Management System (ITMS) in Los Angeles: The ITMS in Los Angeles utilizes sensors, cameras, and data analytics to monitor and control traffic flow on freeways. The system provides real-time traffic information to drivers and adjusts signal timing to optimize traffic flow.
The practical significance of understanding the connection between smart traffic management and transportation green lies in its potential to create more sustainable and livable cities. By reducing congestion, lowering emissions, and improving air quality, smart traffic management systems contribute to a cleaner, healthier, and more efficient transportation system.
Table: Smart Traffic Management and Transportation Green
| Smart Traffic Management | Transportation Green |
|---|---|
| Optimized traffic flow | Reduced congestion |
| Real-time traffic information | Lower emissions |
| Congestion pricing strategies | Improved air quality |
| Enhanced road safety | Enhanced safety |
Green Infrastructure
Green infrastructure plays a crucial role in transportation green by integrating vegetation and other natural elements into transportation systems to mitigate pollution and enhance air quality. This approach offers several environmental and societal benefits that contribute to a more sustainable and livable transportation system.
The significance of green infrastructure as a component of transportation green stems from its ability to:
- Reduce Air Pollution: Green infrastructure, such as trees and green walls, can absorb air pollutants, including particulate matter and nitrogen oxides, improving air quality and reducing respiratory health risks.
- Mitigate Urban Heat Island Effect: Vegetation provides shade and evapotranspiration, which can lower temperatures in urban areas, reducing the urban heat island effect and improving thermal comfort.
- Enhance Stormwater Management: Green infrastructure can help manage stormwater runoff by absorbing and filtering rainwater, reducing the risk of flooding and improving water quality.
- Promote Biodiversity: Green infrastructure provides habitats for wildlife, supporting biodiversity and ecological balance in urban environments.
Real-life examples of green infrastructure in transportation systems include:
- Green Roofs on Bus Shelters: Bus shelters with green roofs can reduce air pollution, provide shade for commuters, and improve the overall aesthetics of urban areas.
- Bioswales along Highways: Bioswales are vegetated channels that can filter stormwater runoff from highways, removing pollutants and protecting water quality.
- Tree-lined Streets: Planting trees along streets can provide shade, absorb air pollution, and enhance the overall livability of urban neighborhoods.
The practical significance of understanding the connection between green infrastructure and transportation green lies in its potential to create healthier, more sustainable, and more resilient communities. By incorporating green infrastructure into transportation systems, we can improve air quality, mitigate climate change, and enhance the overall quality of life for urban residents.
Table: Green Infrastructure and Transportation Green
| Green Infrastructure | Transportation Green |
|---|---|
| Reduces air pollution | Improved air quality |
| Mitigates urban heat island effect | Reduced thermal discomfort |
| Enhances stormwater management | Reduced flooding risk and improved water quality |
| Promotes biodiversity | Enhanced ecological balance |
FAQs on “Transportation Green”
This section addresses frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to “transportation green” to provide a comprehensive understanding of its key aspects and importance.
Question 1: What is the significance of “transportation green”?
Transportation green encompasses a range of approaches and technologies that aim to reduce the environmental impact of transportation systems, such as promoting electric vehicles, encouraging public transportation, and incorporating green infrastructure into transportation networks.
Question 2: How does “transportation green” contribute to environmental sustainability?
Transportation green strategies, such as transitioning to electric vehicles and promoting renewable energy sources, help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution, mitigating climate change and improving air quality.
Question 3: What are the economic benefits of “transportation green”?
Transportation green initiatives can lead to cost savings for individuals and businesses through reduced fuel consumption, lower maintenance costs for electric vehicles, and improved energy efficiency.
Question 4: How does “transportation green” impact public health?
Transportation green measures, such as promoting walking and biking, and reducing air pollution, contribute to improved public health by encouraging physical activity and enhancing air quality.
Question 5: What are the challenges associated with implementing “transportation green” initiatives?
Challenges include high upfront costs, infrastructure limitations, and the need for behavioral changes. However, long-term benefits and government incentives can help overcome these challenges.
Question 6: What is the future outlook for “transportation green”?
Transportation green is expected to continue gaining momentum as technological advancements, increased awareness, and government support drive the transition towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation systems.
In summary, transportation green is a vital approach to addressing environmental concerns, improving public health, and promoting economic sustainability in the transportation sector. By embracing transportation green initiatives, we can create a cleaner, healthier, and more sustainable future for our planet and its inhabitants.
Transition to the next article section:
Tips for Embracing “Transportation Green”
Adopting transportation green practices can contribute significantly to environmental sustainability and personal well-being. Here are some practical tips to help you incorporate transportation green into your daily life:
Tip 1: Opt for Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) produce zero tailpipe emissions, reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Consider EVs as your next vehicle purchase or lease to make a positive environmental impact.
Tip 2: Utilize Public Transportation
Public transportation systems, such as buses, trains, and subways, reduce the number of vehicles on the road, leading to less traffic congestion and lower emissions. Embrace public transportation whenever possible, especially during peak hours.
Tip 3: Walk or Bike for Short Distances
Walking or biking for short distances is a great way to reduce your carbon footprint while also incorporating physical activity into your routine. Consider walking or biking to work, school, or nearby errands.
Tip 4: Implement Ride-Sharing
Ride-sharing services connect passengers with drivers traveling in a similar direction, reducing the number of single-occupancy vehicles on the road. Utilize ride-sharing apps to share your commute or for occasional trips.
Tip 5: Invest in Green Infrastructure
Green infrastructure, such as trees and green roofs, can help mitigate air pollution, reduce the urban heat island effect, and improve stormwater management. Support initiatives to incorporate green infrastructure into your community’s transportation systems.
Tip 6: Choose Fuel-Efficient Vehicles
If opting for an electric vehicle is not immediately feasible, consider choosing a fuel-efficient gasoline or hybrid vehicle. Look for vehicles with high MPG ratings and advanced fuel-saving technologies.
Tip 7: Practice Eco-Driving Techniques
Eco-driving techniques, such as smooth acceleration, avoiding rapid braking, and maintaining optimal tire pressure, can improve your vehicle’s fuel efficiency. Adopt these techniques to reduce your fuel consumption and environmental impact.
Summary:
Incorporating transportation green practices into your daily routine not only benefits the environment but also contributes to your personal well-being. By embracing these tips, you can reduce your carbon footprint, improve air quality, and promote a more sustainable and healthy transportation system for all.
Conclusion
Transportation green encompasses a multitude of approaches and technologies aimed at reducing the environmental impact of transportation systems. By promoting electric vehicles, encouraging public transportation, and incorporating green infrastructure, we can create a cleaner, healthier, and more sustainable future for our planet and its inhabitants.
Embracing transportation green practices is not merely an environmental obligation but also a personal and collective responsibility. Every small step, from choosing an electric vehicle to opting for public transportation, contributes to a larger movement towards a more sustainable transportation system. As we continue to innovate and adopt transportation green solutions, we pave the way for a greener, healthier, and more equitable future for generations to come.
Youtube Video: