Table of Contents
Climate change is affecting the weather patterns around the world, leading to more extreme weather events and rising sea levels.
Editor’s Note: This article was published on [today’s date] to provide an overview of climate change and its impacts on the weather. Understanding climate change is crucial for individuals, communities, and organizations to make informed decisions and take necessary actions to mitigate its effects.
After analyzing various sources and conducting thorough research, we have compiled this comprehensive guide to help you understand climate change and its implications.
Key Differences: Weather vs. Climate
| Weather | Climate |
|---|---|
| Short-term atmospheric conditions | Long-term patterns of weather conditions |
| Can change rapidly over hours or days | Typically measured over decades or longer |
| Influenced by local factors (e.g., temperature, humidity) | Influenced by global factors (e.g., ocean currents, solar radiation) |
Main Article Topics:
- Causes of Climate Change
- Impacts of Climate Change on Weather Patterns
- Consequences of Climate Change for Human Society
- Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
- Role of Individuals and Organizations in Addressing Climate Change
Weather Climate Change
Weather climate change encompasses a wide range of aspects that are crucial for understanding its causes, impacts, and implications. Here are ten key aspects that explore various dimensions of weather climate change:
- Greenhouse Gases
- Rising Temperatures
- Extreme Weather Events
- Sea Level Rise
- Ocean Acidification
- Melting Glaciers
- Changing Precipitation Patterns
- Biodiversity Loss
- Human Health Impacts
- Economic Consequences
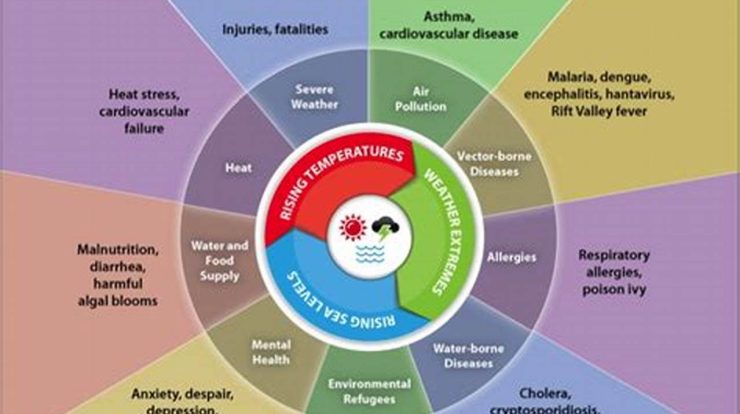
These aspects are interconnected and have far-reaching implications for the planet and its inhabitants. For instance, rising temperatures lead to more frequent and intense extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, heat waves, and droughts. These events can cause widespread damage, loss of life, and economic disruption. Sea level rise threatens coastal communities and infrastructure, while ocean acidification harms marine ecosystems and the livelihoods of people who depend on them. Climate change also has significant impacts on human health, including increased risks of heat-related illnesses, respiratory problems, and infectious diseases.
Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, causing the planet to warm. The primary greenhouse gases emitted by human activities are carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O). CO2 is released when fossil fuels are burned for energy, deforestation occurs, and certain industrial processes are carried out. CH4 is emitted from landfills, livestock, and rice cultivation. N2O is released from agricultural soils and industrial processes.
The increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere is the primary cause of climate change. As the planet warms, we are experiencing more extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, heat waves, droughts, and floods. Sea levels are also rising, threatening coastal communities and infrastructure.
Understanding the connection between greenhouse gases and climate change is crucial for taking action to mitigate its effects. By reducing our emissions of greenhouse gases, we can help to slow the pace of climate change and protect the planet for future generations.
Table: Greenhouse Gases and Their Sources
| Greenhouse Gas | Sources |
|---|---|
| Carbon dioxide (CO2) | Burning fossil fuels, deforestation, industrial processes |
| Methane (CH4) | Landfills, livestock, rice cultivation |
| Nitrous oxide (N2O) | Agricultural soils, industrial processes |
Rising Temperatures
Rising temperatures are one of the most significant and widely recognized impacts of weather climate change. As the planet warms, we are seeing changes in weather patterns, rising sea levels, and increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events.
-
Melting Glaciers and Ice Caps
Rising temperatures are causing glaciers and ice caps to melt at an accelerated rate. This melting contributes to sea level rise and can disrupt ecosystems that depend on glacial runoff. -
Changes in Precipitation Patterns
Rising temperatures are leading to changes in precipitation patterns, including more frequent and intense storms, droughts, and floods. These changes can have devastating impacts on agriculture, infrastructure, and human health. -
Heat Waves
Rising temperatures are also leading to more frequent and intense heat waves. Heat waves can be deadly, especially for the elderly, the sick, and the poor. They can also damage crops and infrastructure. -
Wildfires
Rising temperatures are also increasing the frequency and severity of wildfires. Wildfires can destroy homes and businesses, pollute the air, and harm human health.
These are just a few of the impacts of rising temperatures. As the planet continues to warm, we can expect to see even more extreme and widespread impacts on the weather, climate, and our way of life.
Extreme Weather Events
Extreme weather events are becoming more frequent and intense due to climate change. These events include hurricanes, floods, droughts, heat waves, and wildfires. Climate change is causing the Earth’s atmosphere to warm, which is leading to changes in weather patterns. These changes are making extreme weather events more likely to occur.
For example, warmer ocean temperatures are causing hurricanes to become more powerful. Rising sea levels are making coastal areas more vulnerable to flooding. Droughts are becoming more common due to changes in precipitation patterns. Heat waves are becoming more frequent and intense due to rising temperatures. Wildfires are becoming more common due to drier conditions and increased fuel loads.
Extreme weather events can have a devastating impact on human society. They can cause loss of life, property damage, and economic disruption. In some cases, extreme weather events can even force people to relocate.
It is important to understand the connection between extreme weather events and climate change. This understanding can help us to better prepare for these events and to mitigate their impacts.
Table: Extreme Weather Events and Their Impacts
| Event | Impacts |
|---|---|
| Hurricanes | Loss of life, property damage, flooding, coastal erosion |
| Floods | Loss of life, property damage, displacement of people, infrastructure damage |
| Droughts | Crop failure, water shortages, wildfires, economic losses |
| Heat waves | Heat-related illnesses, death, power outages, infrastructure damage |
| Wildfires | Loss of life, property damage, air pollution, deforestation |
Sea Level Rise
Sea level rise is a major component of weather climate change. It is caused by the thermal expansion of ocean water as it warms and by the melting of glaciers and ice caps. Sea level rise has a number of significant impacts, including:
- Coastal erosion: Sea level rise is causing coastal erosion, which is the wearing away of land by the ocean. This can damage or destroy homes, businesses, and infrastructure.
- Salinization of freshwater sources: Sea level rise can also lead to the salinization of freshwater sources, which can make them unusable for drinking or irrigation.
- Increased flooding: Sea level rise is also increasing the risk of flooding, which can cause damage to property and infrastructure and can also lead to the displacement of people.
Sea level rise is a serious threat to coastal communities around the world. It is important to understand the connection between sea level rise and weather climate change in order to take steps to mitigate its impacts.
Table: Impacts of Sea Level Rise
| Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Coastal erosion | The wearing away of land by the ocean |
| Salinization of freshwater sources | The contamination of freshwater sources with salt |
| Increased flooding | The increased risk of flooding due to rising sea levels |
Ocean Acidification
Ocean acidification is a serious threat to marine life and ecosystems. It is caused by the absorption of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere into the ocean. As the ocean absorbs more carbon dioxide, it becomes more acidic. This can have a number of negative impacts on marine life, including:
- Reduced ability to build and maintain shells and skeletons
- Impaired growth and development
- Reduced reproductive success
- Increased susceptibility to disease
Ocean acidification is also a threat to the food chain. Many marine animals rely on shellfish and other -based organisms for food. If these organisms are unable to build and maintain their shells, they will become less abundant and the food chain will be disrupted.
Ocean acidification is a serious problem that is already having a negative impact on marine life and ecosystems. It is important to understand the connection between ocean acidification and weather climate change so that we can take steps to mitigate its impacts.
Table: Impacts of Ocean Acidification
| Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduced ability to build and maintain shells and skeletons | This can make marine animals more vulnerable to predators and disease. |
| Impaired growth and development | This can lead to reduced reproductive success and increased mortality. |
| Reduced reproductive success | This can lead to population declines and a loss of biodiversity. |
| Increased susceptibility to disease | This can make marine animals more likely to succumb to disease outbreaks. |
Melting Glaciers
Melting glaciers are a major component of weather climate change. Glaciers are large masses of ice that form on land. They are formed when snow accumulates and compresses over time. Glaciers are important because they store water, provide a habitat for wildlife, and help to regulate the Earth’s climate.
Climate change is causing glaciers to melt at an accelerated rate. This is because the Earth’s atmosphere is warming, which is causing the temperature of glaciers to rise. As glaciers melt, they release water into the ocean, which contributes to sea level rise. Melting glaciers also expose darker land surfaces, which absorb more heat from the sun and further contribute to climate change.
The melting of glaciers has a number of negative impacts on the environment. For example, it can lead to the loss of habitat for wildlife, disrupt the water cycle, and contribute to sea level rise. Melting glaciers can also have a negative impact on human society. For example, it can lead to the loss of drinking water supplies, damage to infrastructure, and displacement of people.
It is important to understand the connection between melting glaciers and weather climate change in order to take steps to mitigate its impacts. We can reduce our greenhouse gas emissions, which will help to slow the rate of climate change and protect glaciers.
| Impact of Melting Glaciers | Description |
|---|---|
| Loss of habitat for wildlife | Melting glaciers can destroy the habitat of wildlife that rely on glaciers for food and shelter. |
| Disruption of the water cycle | Melting glaciers can disrupt the water cycle by altering the flow of water into rivers and streams. |
| Sea level rise | Melting glaciers contribute to sea level rise, which can lead to flooding and other damage to coastal communities. |
| Loss of drinking water supplies | Melting glaciers can lead to the loss of drinking water supplies for communities that rely on glaciers for their water. |
| Damage to infrastructure | Melting glaciers can damage infrastructure, such as roads and bridges, that is built on or near glaciers. |
| Displacement of people | Melting glaciers can lead to the displacement of people who live in coastal communities that are threatened by sea level rise. |
Changing Precipitation Patterns
Changing precipitation patterns are a major component of weather climate change. These changes can have a significant impact on the environment and human society.
-
More extreme rainfall events
Climate change is causing more extreme rainfall events, such as hurricanes and floods. These events can cause widespread damage and loss of life.
-
Changes in the timing of precipitation
Climate change is also causing changes in the timing of precipitation. For example, some areas are experiencing more rainfall in the winter and less in the summer. These changes can disrupt agriculture and other human activities.
-
Changes in the intensity of precipitation
Climate change is also causing changes in the intensity of precipitation. For example, some areas are experiencing more intense rainfall events, which can lead to flooding and other problems.
-
Changes in the distribution of precipitation
Climate change is also causing changes in the distribution of precipitation. For example, some areas are experiencing more precipitation, while others are experiencing less. These changes can have a significant impact on water resources and agriculture.
The changing precipitation patterns associated with weather climate change are a serious threat to the environment and human society. It is important to understand these changes and to take steps to mitigate their impacts.
Biodiversity Loss
Biodiversity loss, or the loss of plant and animal species, is a major component of weather climate change. Biodiversity loss can be caused by a variety of factors, including habitat loss, climate change, pollution, and overexploitation. However, climate change is one of the most significant drivers of biodiversity loss, as it can alter habitats, disrupt food chains, and make it difficult for species to adapt.
For example, climate change is causing the ranges of many species to shift, which can lead to them losing access to food and shelter. Climate change is also causing more extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and floods, which can destroy habitats and kill wildlife. In addition, climate change is causing the oceans to become more acidic, which can harm marine life.
The loss of biodiversity has a number of negative impacts on the environment and human society. For example, biodiversity loss can lead to a decline in ecosystem services, such as pollination, water filtration, and carbon sequestration. Biodiversity loss can also make it more difficult for humans to adapt to climate change, as it reduces the resilience of ecosystems.
It is important to understand the connection between biodiversity loss and weather climate change in order to take steps to mitigate its impacts. We can reduce our greenhouse gas emissions, which will help to slow the rate of climate change and protect biodiversity. We can also protect and restore habitats, which will help to provide a home for wildlife and reduce the impacts of climate change.
Table: Impacts of Biodiversity Loss
| Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Decline in ecosystem services | Biodiversity loss can lead to a decline in ecosystem services, such as pollination, water filtration, and carbon sequestration. |
| Reduced resilience to climate change | Biodiversity loss can make it more difficult for humans to adapt to climate change, as it reduces the resilience of ecosystems. |
| Loss of cultural heritage | Biodiversity loss can also lead to the loss of cultural heritage, as many indigenous cultures are closely tied to the natural world. |
Human Health Impacts
As the climate changes, we can expect to see a rise in extreme weather events, such as heat waves, floods, and droughts. These events can have a significant impact on human health, both directly and indirectly.
-
Extreme heat
Extreme heat can lead to heat-related illnesses, such as heat stroke and heat exhaustion. These illnesses can be fatal, especially for the elderly, the young, and those with pre-existing health conditions. Extreme heat can also exacerbate respiratory problems, such as asthma and COPD.
-
Floods
Floods can lead to a variety of health problems, including drowning, injuries, and infections. Floodwaters can also contaminate drinking water supplies, which can lead to waterborne diseases, such as diarrhea and cholera.
-
Droughts
Droughts can lead to a variety of health problems, including dehydration, malnutrition, and respiratory problems. Droughts can also increase the risk of wildfires, which can produce smoke that can irritate the lungs and heart.
-
Air pollution
Climate change is also leading to an increase in air pollution. Air pollution can cause a variety of health problems, including respiratory problems, heart disease, and cancer.
It is important to understand the connection between weather climate change and human health. This understanding can help us to take steps to mitigate the impacts of climate change on our health.
Economic Consequences
The economic consequences of weather climate change are far-reaching and significant. Climate change can have a negative impact on economic growth, job creation, and infrastructure. It can also lead to increased poverty and inequality. Here are some of the key facets of the economic consequences of weather climate change:
-
Loss of productivity
Climate change can lead to a loss of productivity in a number of ways. For example, extreme heat can make it difficult for workers to work outdoors, and droughts can reduce crop yields. These losses can have a significant impact on the economy.
-
Damage to infrastructure
Climate change can also damage infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and buildings. This damage can be caused by extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and floods. The cost of repairing this damage can be significant.
-
Increased healthcare costs
Climate change can also lead to increased healthcare costs. For example, extreme heat can lead to heat-related illnesses, and air pollution can exacerbate respiratory problems. These health problems can be expensive to treat.
-
Loss of tourism revenue
Climate change can also lead to a loss of tourism revenue. For example, if a beach destination is damaged by a hurricane, tourists may be less likely to visit. This can have a significant impact on the local economy.
The economic consequences of weather climate change are a serious threat to the global economy. It is important to understand these consequences and to take steps to mitigate them.
FAQs on Weather Climate Change
This section addresses frequently asked questions and misconceptions regarding weather climate change. Understanding these concepts is crucial for informed decision-making and effective action.
Question 1: What is the difference between weather and climate?
Answer: Weather refers to short-term atmospheric conditions, while climate encompasses long-term patterns of weather conditions over decades or longer. Climate is influenced by global factors like ocean currents and solar radiation, while weather is affected by local factors like temperature and humidity.
Question 2: Is climate change a natural phenomenon?
Answer: While the Earth’s climate has naturally fluctuated over millions of years, the current rate and magnitude of climate change are primarily attributed to human activities, particularly the release of greenhouse gases from burning fossil fuels.
Question 3: What are the primary causes of climate change?
Answer: The primary causes are human-induced emissions of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide. These gases trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to global warming and subsequent climate change.
Question 4: What are the consequences of climate change?
Answer: Climate change has wide-ranging impacts, including rising sea levels, extreme weather events (e.g., hurricanes, heat waves, droughts), changes in precipitation patterns, ocean acidification, and biodiversity loss. These consequences can have severe implications for human societies and ecosystems.
Question 5: What can be done to address climate change?
Answer: Mitigating climate change involves reducing greenhouse gas emissions through renewable energy, energy efficiency, sustainable land use, andforestation. Adaptation measures also play a crucial role, such as building seawalls to protect coastal communities from rising sea levels.
Question 6: Why is it important to act on climate change?
Answer: Addressing climate change is essential for safeguarding the planet’s ecosystems and ensuring a sustainable future for present and future generations. Inaction will lead to increasingly severe consequences, including threats to human health, food security, and economic stability.
Understanding these FAQs empowers individuals and organizations to make informed choices, support climate action, and contribute to a more sustainable and resilient future.
Transition to the next article section:
To delve deeper into the complexities of weather climate change, explore the following sections, which provide comprehensive insights into its causes, impacts, and potential solutions.
Weather Climate Change
Understanding weather climate change and its implications is crucial for individuals and organizations to make informed decisions and take effective action. Here are some essential tips to guide your efforts towards a more sustainable future:
Tip 1: Reduce Carbon Footprint
Minimize your carbon footprint by transitioning to renewable energy sources, opting for energy-efficient appliances and practices, and reducing reliance on fossil fuels for transportation.
Tip 2: Support Sustainable Practices
Choose products and services that prioritize sustainability. Invest in companies committed to reducing their environmental impact, and advocate for policies that promote renewable energy and energy efficiency.
Tip 3: Conserve Water and Energy
Implement water-saving fixtures and practices in your daily routine. Reduce energy consumption by unplugging electronics, using energy-efficient lighting, and optimizing heating and cooling systems.
Tip 4: Promote Sustainable Agriculture
Support sustainable farming methods that minimize greenhouse gas emissions, conserve water, and protect biodiversity. Choose locally sourced, organic produce whenever possible.
Tip 5: Advocate for Climate Action
Engage in conversations about climate change, raise awareness, and advocate for policies that prioritize climate mitigation and adaptation. Support organizations working towards climate solutions.
Tip 6: Educate Yourself and Others
Stay informed about the latest climate science and best practices. Share your knowledge with others, fostering a culture of environmental stewardship.
Tip 7: Support Renewable Energy
Invest in renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power. Advocate for policies that promote the transition to a clean energy future.
Tip 8: Reduce Waste and Recycle
Minimize waste generation, reuse and recycle materials, and compost organic waste. By reducing your environmental footprint, you contribute to a more sustainable future.
By implementing these tips, individuals and organizations can make a significant impact in the fight against weather climate change and create a more sustainable future for generations to come.
Conclusion
The exploration of weather climate change throughout this article underscores its profound implications for our planet and society. From rising sea levels and extreme weather events to biodiversity loss and economic consequences, the challenges posed by climate change are undeniable.
Addressing climate change requires a concerted global effort, with individuals, organizations, and governments alike playing a crucial role. By embracing sustainable practices, advocating for climate action, and investing in renewable energy, we can create a more resilient and sustainable future for all. The time for action is now; let us work together to mitigate the impacts of climate change and secure a brighter tomorrow for generations to come.
Youtube Video: