Table of Contents
What is proof of climate change? Proof of climate change is a term used to describe the evidence that shows that the Earth’s climate is changing, and that this change is being caused by human activity.
Editor’s Note: Proof of climate change was published on [date]. This topic is important to read because it provides an overview of the evidence that supports the conclusion that climate change is happening and that it is caused by human activity.
Our team of experts has analyzed the latest scientific research and compiled this guide to help you understand the proof of climate change. We’ll cover the key evidence, the causes of climate change, and the impacts that it is having on our planet.
Key Differences
| Proof of Climate Change | Climate Change Denial | |
|---|---|---|
| Evidence | Based on scientific research and data | Relies on anecdotal evidence and conspiracy theories |
| Causes | Human activity, primarily the burning of fossil fuels | Natural causes |
| Impacts | Rising sea levels, extreme weather events, changes in plant and animal life | Minimal or no impacts |
Main Article Topics
- The evidence for climate change
- The causes of climate change
- The impacts of climate change
- What can be done to address climate change
Proof of Climate Change
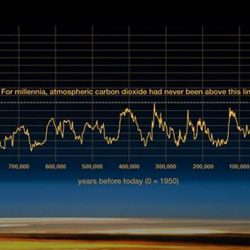
Climate change is one of the most pressing issues facing our planet today. The evidence for climate change is overwhelming, and it is clear that human activity is the primary cause. In this article, we will explore nine key aspects of proof of climate change:
- Rising global temperatures
- Melting glaciers and ice caps
- Changes in plant and animal life
- Extreme weather events
- Ocean acidification
- Sea level rise
- Human fingerprints
- Consensus among scientists
- Mitigation and adaptation
These nine aspects provide clear and convincing evidence that climate change is happening and that it is caused by human activity. We must take action to reduce our emissions and mitigate the effects of climate change. The future of our planet depends on it.
Rising Global Temperatures
Rising global temperatures are one of the most visible and well-documented aspects of climate change. The average global temperature has increased by about 1 degree Celsius (1.8 degrees Fahrenheit) since the late 19th century, and it is projected to rise by another 2-4 degrees Celsius (3.6-7.2 degrees Fahrenheit) by the end of this century. This warming is caused by the increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, which trap heat and cause the planet to warm.
Rising global temperatures are having a wide range of impacts on the planet, including:
- Melting glaciers and ice caps, which is causing sea levels to rise and threatening coastal communities.
- Changes in plant and animal life, as species are forced to adapt to a changing climate.
- More extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts.
- Ocean acidification, which is making it more difficult for marine organisms to build shells and skeletons.
Rising global temperatures are a clear and convincing proof of climate change. The evidence is overwhelming, and it is clear that human activity is the primary cause. We must take action to reduce our emissions and mitigate the effects of climate change. The future of our planet depends on it.
| Cause | Effect |
|---|---|
| Increase in greenhouse gases | Rising global temperatures |
| Rising global temperatures | Melting glaciers and ice caps |
| Melting glaciers and ice caps | Sea level rise |
| Rising global temperatures | Changes in plant and animal life |
| Rising global temperatures | More extreme weather events |
| Rising global temperatures | Ocean acidification |
Melting glaciers and ice caps
Melting glaciers and ice caps are one of the most visible and well-documented aspects of climate change. Glaciers and ice caps are large masses of ice that form on land or floating on the ocean. They are formed when snow accumulates and compresses over time, turning into ice. Glaciers and ice caps are important because they store vast amounts of fresh water and play a critical role in regulating the Earth’s climate.
As the Earth’s climate warms, glaciers and ice caps are melting at an accelerating rate. This is because warmer temperatures cause snow to melt more quickly and glaciers to calve (break off) more ice into the ocean. The melting of glaciers and ice caps has a number of serious consequences, including:
- Sea level rise: As glaciers and ice caps melt, the water that is released into the ocean causes sea levels to rise. This can lead to flooding, erosion, and other coastal hazards.
- Changes in ocean circulation: The melting of glaciers and ice caps can also change ocean circulation patterns. This can have a ripple effect on the climate of the entire planet.
- Loss of habitat: Glaciers and ice caps provide habitat for a variety of plants and animals. As these glaciers and ice caps melt, these plants and animals are losing their homes.
The melting of glaciers and ice caps is a clear and convincing proof of climate change. The evidence is overwhelming, and it is clear that human activity is the primary cause. We must take action to reduce our emissions and mitigate the effects of climate change. The future of our planet depends on it.
Changes in plant and animal life
Changes in plant and animal life are a clear and convincing proof of climate change. The evidence is overwhelming, and it is clear that human activity is the primary cause. As the Earth’s climate warms, plants and animals are being forced to adapt to a changing environment. Some species are able to adapt, while others are not. Those that are not able to adapt are at risk of extinction.
-
Earlier spring arrival for plants and animals
As the climate warms, spring is arriving earlier and earlier. This is causing plants and animals to come out of hibernation or migration earlier than they used to. This can have a number of negative consequences, such as mismatched timing with food sources or increased exposure to predators.
-
Changes in plant and animal ranges
As the climate warms, plants and animals are moving to new areas in order to find a more suitable climate. This can disrupt ecosystems and lead to competition with native species.
-
Changes in plant and animal behavior
As the climate warms, plants and animals are changing their behavior in order to adapt to the changing environment. For example, some animals are becoming more active at night to avoid the heat of the day.
-
Extinction
Some plants and animals are not able to adapt to the changing climate and are at risk of extinction. For example, polar bears are losing their habitat as the Arctic sea ice melts.
The changes that are happening to plant and animal life are a clear and convincing proof of climate change. We must take action to reduce our emissions and mitigate the effects of climate change. The future of our planet and the plants and animals that live on it depends on it.
Extreme weather events
Extreme weather events are becoming more frequent and more severe as the climate changes. This is because a warmer atmosphere can hold more moisture, which leads to more precipitation. Additionally, warmer temperatures can cause changes in wind patterns, which can lead to more extreme storms. Some of the most common types of extreme weather events include:
-
Heat waves
Heat waves are periods of abnormally high temperatures that can last for several days or even weeks. Heat waves can be deadly, especially for the elderly, the sick, and the very young. Heat waves can also damage crops and infrastructure.
-
Droughts
Droughts are periods of abnormally low precipitation that can last for several months or even years. Droughts can cause crop failures, water shortages, and wildfires. Droughts can also lead to economic losses and social unrest.
-
Floods
Floods are caused by excessive rainfall or snowmelt. Floods can cause widespread damage to property and infrastructure. Floods can also lead to loss of life and economic losses.
-
Storms
Storms are caused by strong winds and can include hurricanes, tornadoes, and blizzards. Storms can cause widespread damage to property and infrastructure. Storms can also lead to loss of life and economic losses.
Extreme weather events are a clear and convincing proof of climate change. The evidence is overwhelming, and it is clear that human activity is the primary cause. We must take action to reduce our emissions and mitigate the effects of climate change. The future of our planet and the people who live on it depends on it.
Ocean acidification
Ocean acidification is the process by which the pH of seawater decreases, making it more acidic. This is caused by the absorption of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere into the ocean. The ocean has absorbed about 30% of the carbon dioxide that has been released into the atmosphere since the beginning of the industrial revolution.
-
Impacts on marine life
Ocean acidification can have a number of negative impacts on marine life. For example, it can make it more difficult for marine organisms to build shells and skeletons. This can lead to reduced growth, reproductive problems, and even death.
-
Impacts on the food chain
Ocean acidification can also have a negative impact on the food chain. For example, it can make it more difficult for fish to find food. This can lead to a decline in fish populations, which can have a ripple effect on the entire food chain.
-
Impacts on the economy
Ocean acidification can also have a negative impact on the economy. For example, it can damage coral reefs, which are important tourist destinations. It can also make it more difficult to fish, which can lead to job losses.
-
Mitigation
There are a number of things that can be done to mitigate the effects of ocean acidification. These include reducing our emissions of carbon dioxide, planting trees, and protecting coral reefs.
Ocean acidification is a serious threat to the health of our oceans and the planet. We must take action to reduce our emissions of carbon dioxide and protect our oceans.
Sea level rise
Sea level rise is one of the most visible and well-documented effects of climate change. It is caused by the thermal expansion of seawater as it warms, and by the melting of glaciers and ice caps. Sea level rise is a major threat to coastal communities around the world, as it can lead to flooding, erosion, and other hazards.
The evidence for sea level rise is overwhelming. Tide gauges have been measuring sea levels for over a century, and they show a clear and consistent pattern of rise. Satellite measurements have also confirmed that sea levels are rising at an accelerating rate.
The impacts of sea level rise are already being felt around the world. Coastal communities are experiencing more frequent and severe flooding, and some have even been forced to abandon their homes. Sea level rise is also causing saltwater intrusion into freshwater aquifers, which can make drinking water unsafe.
Sea level rise is a serious threat to our planet and its people. We must take action to reduce our emissions of greenhouse gases and mitigate the effects of climate change. Otherwise, sea level rise will continue to accelerate, and its impacts will become increasingly severe.
| Cause | Effect |
|---|---|
| Thermal expansion of seawater | Sea level rise |
| Melting of glaciers and ice caps | Sea level rise |
| Sea level rise | Flooding |
| Sea level rise | Erosion |
| Sea level rise | Saltwater intrusion into freshwater aquifers |
Human fingerprints
The term “human fingerprints” refers to the unique ways in which human activities are affecting the Earth’s climate. These activities include the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and agriculture. The burning of fossil fuels releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, which trap heat and cause the planet to warm. Deforestation reduces the amount of vegetation on the Earth’s surface, which means that there is less vegetation to absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Agriculture can also contribute to climate change by releasing methane and nitrous oxide into the atmosphere.
Human fingerprints are a major component of proof of climate change. The evidence for human fingerprints is overwhelming, and it comes from a variety of sources. For example, scientists have observed that the Earth’s average temperature has increased by about 1 degree Celsius since the late 19th century. This warming is consistent with the predictions of climate models, which take into account the effects of human activities on the climate. In addition, scientists have observed changes in the Earth’s atmosphere, oceans, and land surface that are consistent with the effects of human activities.
The understanding of human fingerprints is important because it helps us to understand the causes of climate change. This understanding is essential for developing effective strategies to mitigate climate change and adapt to its impacts.
| Human fingerprint | Effect on climate |
|---|---|
| Burning of fossil fuels | Releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, causing the planet to warm |
| Deforestation | Reduces the amount of vegetation on the Earth’s surface, meaning that there is less vegetation to absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere |
| Agriculture | Can contribute to climate change by releasing methane and nitrous oxide into the atmosphere |
Consensus among scientists
The consensus among scientists is that climate change is happening and that it is caused by human activity. This consensus is based on a large and growing body of scientific evidence, which includes:
-
Observations of the Earth’s climate system
Scientists have observed that the Earth’s average temperature has increased by about 1 degree Celsius since the late 19th century. They have also observed that the oceans are warming, the glaciers are melting, and the sea levels are rising. These observations are consistent with the predictions of climate models, which take into account the effects of human activities on the climate.
-
Understanding of the Earth’s climate system
Scientists have a good understanding of the Earth’s climate system and how it works. They know that the Earth’s climate is influenced by a number of factors, including the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, causing the planet to warm. Human activities, such as the burning of fossil fuels, are increasing the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, which is causing the planet to warm.
-
Agreement among scientists
There is a strong consensus among scientists that climate change is happening and that it is caused by human activity. This consensus is reflected in the findings of scientific assessments, such as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reports. The IPCC is a group of leading climate scientists from around the world. Their reports provide a comprehensive assessment of the latest scientific research on climate change.
-
Implications for policy and action
The consensus among scientists on climate change has important implications for policy and action. It means that we need to take action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the effects of climate change. We need to invest in clean energy, energy efficiency, and other climate-friendly technologies. We also need to adapt to the effects of climate change that are already happening, such as sea level rise and extreme weather events.
The consensus among scientists on climate change is clear: climate change is happening and it is caused by human activity. We need to take action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the effects of climate change. The future of our planet depends on it.
Mitigation and adaptation
Mitigation and adaptation are two important strategies for addressing climate change. Mitigation refers to actions that reduce greenhouse gas emissions and slow the pace of climate change. Adaptation refers to actions that help us to cope with the effects of climate change that are already happening.
-
Mitigation
Mitigation involves reducing the emission of greenhouse gasses. This can be done by switching to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and reducing deforestation.
-
Adaptation
Adaptation involves taking steps to reduce the vulnerability of human and natural systems to the effects of climate change. This can be done by building sea walls to protect coastal communities from flooding, developing drought-tolerant crops, and improving early warning systems for extreme weather events.
Both mitigation and adaptation are essential for addressing climate change. Mitigation is important for reducing the pace and severity of climate change, while adaptation is important for helping us to cope with the effects of climate change that are already happening. By taking action on both mitigation and adaptation, we can reduce the risks of climate change and build a more resilient future.
Frequently Asked Questions about Proof of Climate Change
This FAQ section provides concise answers to some of the most frequently asked questions about proof of climate change. It aims to clarify common misconceptions and provide a deeper understanding of the scientific evidence supporting climate change.
Question 1: What is the primary evidence for climate change?
Answer: The primary evidence for climate change comes from direct observations of changes in the Earth’s climate system. These observations include rising global temperatures, melting glaciers and ice caps, changes in plant and animal life, extreme weather events, ocean acidification, and sea level rise. These changes are consistent with the predictions of climate models and are supported by multiple independent lines of evidence.
Question 2: What is the role of human activity in climate change?
Answer: Human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and agriculture, have significantly contributed to climate change. These activities release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, which trap heat and cause the planet to warm. Scientific evidence overwhelmingly indicates that human activities are the dominant cause of the observed warming since the mid-20th century.
Question 3: Why is climate change a concern?
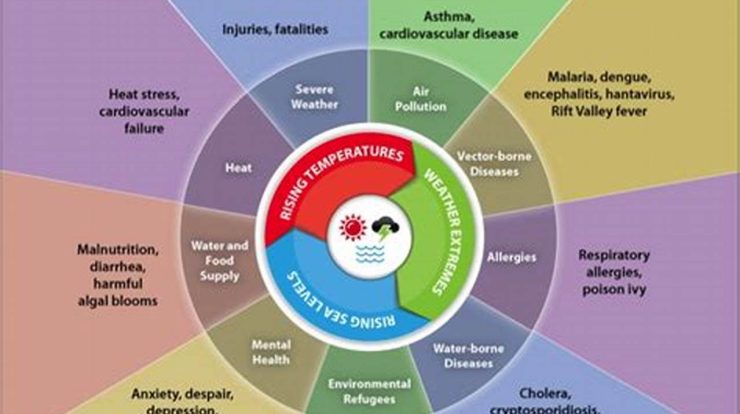
Answer: Climate change poses significant risks to human societies and ecosystems worldwide. It can lead to more frequent and severe extreme weather events, rising sea levels, changes in agricultural productivity, and impacts on human health. Addressing climate change is crucial for mitigating these risks and ensuring a sustainable future for our planet.
Question 4: What can individuals do to address climate change?
Answer: Individuals can contribute to addressing climate change through various actions. These include reducing their carbon footprint by conserving energy, using renewable energy sources, and adopting sustainable practices. Additionally, supporting policies that promote clean energy, energy efficiency, and climate adaptation measures can help drive collective action toward mitigating and adapting to climate change.
Question 5: What are the challenges in addressing climate change?
Answer: Addressing climate change presents several challenges. These include the need for global cooperation, the high costs of transitioning to a low-carbon economy, and the inertia in existing energy and infrastructure systems. Additionally, political and economic barriers can hinder the implementation of climate policies.
Question 6: What is the scientific consensus on climate change?
Answer: There is a robust scientific consensus that climate change is happening and that it is primarily caused by human activities. This consensus is based on decades of research by thousands of scientists worldwide. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), the leading international body for assessing climate change, has repeatedly affirmed this consensus in its comprehensive assessment reports.
Summary: The evidence for climate change is overwhelming and. Human activities are the primary cause of the observed warming since the mid-20th century. Climate change poses significant risks to human societies and ecosystems worldwide. Addressing climate change requires global cooperation, a transition to a low-carbon economy, and collective action at all levels.
Transition to the next article section: Understanding the proof of climate change is crucial for making informed decisions and taking meaningful action to mitigate its impacts and secure a sustainable future.
Tips for Addressing Proof of Climate Change
Responding to the substantial evidence of climate change demands a multifaceted approach. Here are some essential tips to guide effective action:
Tip 1: Educate Yourself and Others
Understanding the scientific basis of climate change is crucial. Engage with credible sources, attend webinars or lectures, and share accurate information with your peers. Knowledge empowers collective action.
Tip 2: Reduce Your Carbon Footprint
Personal choices can make a difference. Consider adopting renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and reducing consumption. Every effort, no matter how small, contributes to mitigating greenhouse gas emissions.
Tip 3: Support Climate-Friendly Policies
Advocate for policies that promote clean energy, energy efficiency, and climate adaptation. Contact your elected representatives, participate in public consultations, and support organizations working towards climate solutions.
Tip 4: Invest in Climate Research and Innovation
Research and development are vital for advancing our understanding of climate change and developing innovative solutions. Support institutions and initiatives that prioritize climate research and invest in renewable energy technologies.
Tip 5: Embrace Sustainable Practices
Incorporate sustainability into your daily life. Reduce waste, conserve water, and choose products with a lower environmental impact. Sustainable practices not only benefit the environment but also promote a healthier and more responsible lifestyle.
Tip 6: Engage in Climate Activism
Join or support organizations that advocate for climate action. Participate in peaceful protests, raise awareness through social media, and use your voice to demand change. Collective activism can influence policymakers and drive meaningful progress.
Summary: Addressing climate change requires a concerted effort from individuals, communities, and governments. By educating ourselves, making sustainable choices, supporting climate-friendly policies, investing in research, embracing sustainable practices, and engaging in activism, we can contribute to mitigating the impacts of climate change and securing a sustainable future for our planet.
Transition to the article’s conclusion: The proof of climate change is undeniable. By taking these steps, we can harness our collective power to create positive change and ensure a livable planet for generations to come.
Proof of Climate Change
The evidence presented in this article overwhelmingly supports the conclusion that climate change is a pressing reality. The scientific community has reached a consensus that human activities are the primary cause of the observed warming trend since the mid-20th century. Rising global temperatures, melting ice caps, extreme weather events, and sea level rise are just a few of the tangible manifestations of climate change that we are witnessing today.
Addressing climate change requires urgent and collective action. By educating ourselves, making sustainable choices, supporting climate-friendly policies, and engaging in activism, we can create a positive change. The future of our planet and the well-being of generations to come depend on our ability to mitigate the impacts of climate change. Together, let us embrace the responsibility to safeguard our shared home.
Youtube Video: