Table of Contents
How much do you know about the environmental effects of climate change?
Environmental effects of climate change are a growing concern due to affecting our environment and the world around us!
Editor’s Notes: “Environmental effects climate change” was published today because this topic is important to know its impact on today’s world.
To help raise awareness of the environmental effects of climate change, we’ve put together this guide. In this guide, we’ll discuss the causes and effects of climate change, as well as what can be done to mitigate its impacts.
Key differences or Key takeways:
| Cause | Effects |
|---|---|
Greenhouse gasses increase in the atmosphere | Rising global temperatures |
Burning fossil fuels | More extreme weather events |
Deforestation | Sea level rise |
Transition to main article topics:
In this guide, we’ll cover the following topics:
- The causes of climate change
- The effects of climate change
- What can be done to mitigate the impacts of climate change
Environmental Effects of Climate Change
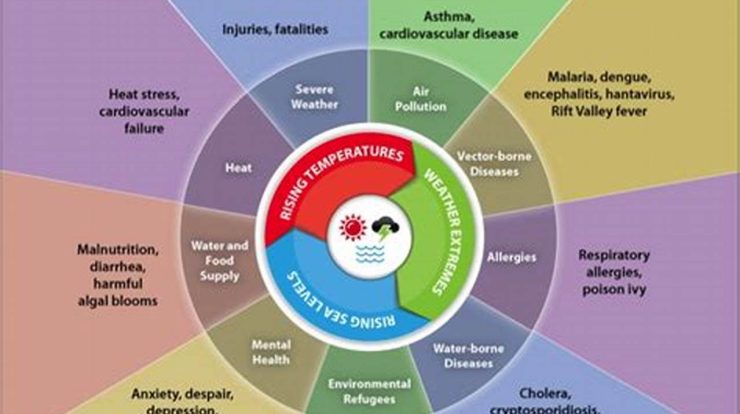
Climate change is one of the most pressing issues facing our planet today. The environmental effects of climate change are far-reaching and include:
- Rising global temperatures
- More extreme weather events
- Sea level rise
- Ocean acidification
- Loss of biodiversity
- Changes in plant and animal distributions
- Increased risk of droughts and floods
- Melting of glaciers and ice caps
- Permafrost thaw
- Changes in ocean currents
These are just a few of the key environmental effects of climate change, and their impacts are already being felt around the world. Rising global temperatures are leading to more extreme weather events such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts. Sea level rise is threatening coastal communities and infrastructure. Ocean acidification is making it difficult for marine organisms to build shells and skeletons. The loss of biodiversity is reducing the resilience of ecosystems to climate change.The environmental effects of climate change are a serious threat to our planet and its people. We need to take action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Rising global temperatures
Rising global temperatures are one of the most significant environmental effects of climate change. The Earth’s average temperature has increased by about 1 degree Celsius since the late 19th century, and it is projected to rise by another 2-4 degrees Celsius by the end of this century. This warming is caused by the increasing levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, which trap heat and cause the planet to warm.
Rising global temperatures have a wide range of environmental effects, including:
- More extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts
- Sea level rise, which threatens coastal communities and infrastructure
- Changes in plant and animal distributions
- Loss of biodiversity
- Melting of glaciers and ice caps
- Permafrost thaw
- Changes in ocean currents
These effects are already being felt around the world. For example, the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events has increased in recent years, and sea levels are rising at an accelerating rate. The melting of glaciers and ice caps is also contributing to sea level rise and is threatening the water supplies of millions of people.
Rising global temperatures are a serious threat to our planet and its people. We need to take action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Table: Rising Global Temperatures and Environmental Effects
| Rising Global Temperatures | Environmental Effects |
|---|---|
| Causes | Increased greenhouse gas emissions |
| Impacts | More extreme weather events, sea level rise, changes in plant and animal distributions, loss of biodiversity, melting of glaciers and ice caps, permafrost thaw, changes in ocean currents |
| Consequences | Threats to human health, safety, and well-being; damage to infrastructure and property; loss of ecosystems and biodiversity; economic losses |
More extreme weather events
More extreme weather events are one of the most significant environmental effects of climate change. As the Earth’s atmosphere warms, it can hold more water vapor, which leads to more frequent and intense storms. Additionally, rising sea levels are making coastal areas more vulnerable to flooding and storm surges.
-
Increased frequency and intensity of storms
Climate change is causing storms to become more frequent and intense. For example, the number of Category 4 and 5 hurricanes has increased in recent years. These storms can cause widespread damage and loss of life.
-
More extreme precipitation events
Climate change is also leading to more extreme precipitation events, such as floods and droughts. These events can cause widespread damage to infrastructure and agriculture, and can also lead to loss of life.
-
Heat waves
Heat waves are becoming more frequent and intense due to climate change. These events can be deadly, especially for the elderly and those with pre-existing health conditions.
-
Droughts
Droughts are also becoming more common and severe due to climate change. These events can cause widespread crop failures and water shortages.
More extreme weather events are a serious threat to human health, safety, and well-being. They can also cause significant damage to infrastructure and property. It is important to take action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the impacts of climate change in order to reduce the risk of more extreme weather events.
Sea level rise
Sea level rise is one of the most significant environmental effects of climate change. As the Earth’s atmosphere warms, the oceans expand and glaciers and ice caps melt, adding water to the oceans and causing sea levels to rise. Sea level rise is a major threat to coastal communities and infrastructure, and it can also have a significant impact on ecosystems and biodiversity.
-
Coastal erosion
Sea level rise is causing coastal erosion, which is the wearing away of land by the action of waves, currents, and tides. Coastal erosion can damage or destroy homes, businesses, and infrastructure, and it can also lead to the loss of beaches and other natural habitats.
-
Flooding
Sea level rise is also increasing the risk of flooding in coastal areas. Flooding can damage or destroy homes, businesses, and infrastructure, and it can also lead to the loss of life. Flooding can also contaminate drinking water sources and spread disease.
-
Salinization
Sea level rise is causing saltwater to intrude into freshwater aquifers and estuaries. This can make drinking water sources unusable and can also damage crops and other vegetation. Salinization can also harm fish and other aquatic life.
-
Loss of habitat
Sea level rise is causing the loss of habitat for many coastal plants and animals. This can disrupt ecosystems and lead to the loss of biodiversity. Sea level rise can also force people to relocate, which can disrupt communities and economies.
Sea level rise is a serious threat to coastal communities and ecosystems around the world. It is important to take action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the impacts of climate change in order to reduce the risk of sea level rise.
Ocean acidification
Ocean acidification is a serious environmental threat caused by the increasing levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. As the ocean absorbs carbon dioxide, it becomes more acidic, which can have a devastating impact on marine life.
-
Impacts on marine organisms
Ocean acidification can damage the shells and skeletons of marine organisms, making them more vulnerable to predators and disease. It can also interfere with their ability to reproduce and grow.
-
Impacts on coral reefs
Coral reefs are particularly vulnerable to ocean acidification. Acidic water can dissolve the calcium carbonate that corals use to build their skeletons, causing them to bleach and die.
-
Impacts on fisheries
Ocean acidification can have a negative impact on fisheries. Acidic water can make it more difficult for fish to find food and reproduce. It can also lead to the loss of habitat, as coral reefs and other marine ecosystems are damaged.
-
Impacts on the global food chain
Ocean acidification can have a ripple effect on the global food chain. Marine organisms are an important food source for humans and other animals. If ocean acidification damages marine ecosystems, it could have a negative impact on the food supply.
Ocean acidification is a serious threat to the health of our oceans and the planet. It is important to take action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the impacts of climate change in order to protect our oceans and the marine life that depends on them.
Loss of biodiversity
Loss of biodiversity is a major environmental problem that is closely linked to climate change. Climate change is causing the extinction of species at an accelerated rate, and it is also disrupting the delicate balance of ecosystems around the world.
There are many ways in which climate change can lead to the loss of biodiversity. For example, rising temperatures can make it difficult for some species to survive, and changes in precipitation patterns can disrupt the food chain. Additionally, climate change can cause the loss of habitat, as species are forced to move to new areas in search of food and shelter.
The loss of biodiversity has a number of negative consequences. For example, it can lead to the decline of ecosystem services, such as pollination and water purification. It can also make it more difficult for humans to adapt to climate change, as we rely on biodiversity for food, medicine, and other resources.
It is important to take action to reduce climate change and protect biodiversity. We can do this by reducing our greenhouse gas emissions, investing in renewable energy, and protecting natural habitats.
Table: Loss of Biodiversity and Environmental Effects of Climate Change
| Loss of Biodiversity | Environmental Effects of Climate Change |
|---|---|
| Extinction of species | Rising temperatures |
| Disruption of ecosystems | Changes in precipitation patterns |
| Loss of habitat | Melting of glaciers |
| Decline of ecosystem services | Sea level rise |
| Difficulty adapting to climate change | Ocean acidification |
Changes in plant and animal distributions
Climate change is causing changes in plant and animal distributions around the world. These changes are being driven by a number of factors, including rising temperatures, changes in precipitation patterns, and the loss of habitat.
-
Rising temperatures
Rising temperatures are causing many species to move to higher elevations or latitudes in search of cooler climates. For example, in the United States, the average range of many bird species has shifted northward by about 100 miles over the past 50 years.
-
Changes in precipitation patterns
Changes in precipitation patterns are also affecting plant and animal distributions. For example, in the southwestern United States, many desert plants and animals are moving to higher elevations in search of water. In the southeastern United States, many wetland plants and animals are moving to higher ground in search of drier conditions.
-
Loss of habitat
The loss of habitat is another major factor driving changes in plant and animal distributions. Climate change is causing glaciers and sea ice to melt, which is reducing the amount of habitat available for many Arctic species. In addition, climate change is causing sea levels to rise, which is threatening coastal habitats around the world.
Changes in plant and animal distributions are having a number of negative consequences. For example, these changes can disrupt food chains and ecosystems, and they can lead to the extinction of species. In addition, changes in plant and animal distributions can have a negative impact on human populations, as they can reduce the availability of food and other resources.
It is important to take action to reduce climate change and protect plant and animal distributions. We can do this by reducing our greenhouse gas emissions, investing in renewable energy, and protecting natural habitats.
Increased risk of droughts and floods
Climate change is increasing the risk of droughts and floods around the world. Droughts occur when there is a prolonged period of below-average precipitation, while floods occur when there is a large amount of precipitation in a short period of time. Both droughts and floods can have devastating impacts on human populations and ecosystems.
Droughts can cause crop failures, water shortages, and wildfires. They can also lead to economic losses and social unrest. Floods can cause property damage, infrastructure damage, and loss of life. They can also contaminate water supplies and spread disease.
The increased risk of droughts and floods is a major concern for many communities around the world. It is important to understand the causes and effects of droughts and floods in order to develop strategies to mitigate their impacts.
Table: Increased Risk of Droughts and Floods and Environmental Effects of Climate Change
| Increased Risk of Droughts and Floods | Environmental Effects of Climate Change |
|---|---|
| Causes | Rising global temperatures, changes in precipitation patterns |
| Impacts | Crop failures, water shortages, wildfires, property damage, infrastructure damage, loss of life |
| Consequences | Economic losses, social unrest, contamination of water supplies, spread of disease |
Melting of glaciers and ice caps
The melting of glaciers and ice caps is one of the most visible and dramatic effects of climate change. As the Earth’s atmosphere warms, glaciers and ice caps are losing mass at an accelerating rate. This melting is causing sea levels to rise, threatening coastal communities and infrastructure. It is also disrupting ecosystems and contributing to the loss of biodiversity.
The melting of glaciers and ice caps is a major contributor to sea level rise. As glaciers and ice caps melt, the water that is released into the ocean adds to the overall volume of water in the ocean, causing sea levels to rise. Sea level rise is a major threat to coastal communities, as it can lead to flooding, erosion, and other damage to infrastructure and property. It can also displace people and disrupt ecosystems.
The melting of glaciers and ice caps is also disrupting ecosystems and contributing to the loss of biodiversity. Glaciers and ice caps provide habitat for a variety of plants and animals, and they also play an important role in regulating the flow of water and nutrients in ecosystems. As glaciers and ice caps melt, these habitats are lost, and the plants and animals that depend on them are at risk of extinction.
The melting of glaciers and ice caps is a serious threat to the environment and to human populations. It is important to take action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the effects of climate change in order to protect glaciers and ice caps and the ecosystems that depend on them.
Table: Melting of Glaciers and Ice Caps and Environmental Effects of Climate Change
| Melting of Glaciers and Ice Caps | Environmental Effects of Climate Change |
|---|---|
| Causes | Rising global temperatures |
| Impacts | Sea level rise, disruption of ecosystems, loss of biodiversity |
| Consequences | Threats to coastal communities, loss of habitat, extinction of species |
Permafrost thaw
Permafrost thaw is the melting of frozen ground that has remained frozen for at least two consecutive years. It is a significant environmental effect of climate change, as it can release large amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere and disrupt ecosystems.
-
Greenhouse gas emissions
When permafrost thaws, it releases carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere. These greenhouse gases contribute to climate change, which in turn leads to further permafrost thaw. This creates a positive feedback loop that can accelerate climate change.
-
Ecosystem disruption
Permafrost thaw can disrupt ecosystems by altering the physical and chemical properties of the soil. This can make it difficult for plants and animals to survive, and can lead to the loss of biodiversity.
-
Infrastructure damage
Permafrost thaw can also damage infrastructure, such as roads and buildings. This is because the ground becomes unstable as it thaws, which can cause structures to collapse or sink.
-
Water quality impacts
Permafrost thaw can also impact water quality. When permafrost thaws, it can release contaminants into the water supply. These contaminants can pose a health risk to humans and animals.
Permafrost thaw is a serious environmental problem that is being caused by climate change. It is important to take action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the effects of climate change in order to protect permafrost and the ecosystems that depend on it.
Changes in ocean currents
Changes in ocean currents are a significant environmental effect of climate change. Ocean currents play a major role in regulating the Earth’s climate, and changes in these currents can have a far-reaching impact on the environment.
-
Disruption of marine ecosystems
Ocean currents are important for transporting nutrients and oxygen to marine ecosystems. Changes in these currents can disrupt the food chain and lead to the loss of biodiversity.
-
Changes in weather patterns
Ocean currents can also influence weather patterns. Changes in these currents can lead to more extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and floods.
-
Sea level rise
Ocean currents can also affect sea level rise. Changes in these currents can lead to higher sea levels, which can threaten coastal communities and infrastructure.
-
Ocean acidification
Ocean currents can also affect ocean acidification. Changes in these currents can lead to more acidic oceans, which can harm marine life.
Changes in ocean currents are a serious environmental problem that is being caused by climate change. It is important to take action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the effects of climate change in order to protect ocean currents and the ecosystems that depend on them.
FAQs on Environmental Effects of Climate Change
This section addresses frequently asked questions and misconceptions regarding the environmental effects of climate change, providing concise and informative answers.
Question 1: What are the primary environmental effects of climate change?
Climate change has wide-ranging environmental effects, including rising global temperatures, more extreme weather events, sea level rise, ocean acidification, loss of biodiversity, changes in plant and animal distributions, increased risk of droughts and floods, melting of glaciers and ice caps, permafrost thaw, and changes in ocean currents.
Question 2: How does climate change contribute to the increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events?
As the Earth’s atmosphere warms, it holds more water vapor, leading to more frequent and intense storms, such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts. Rising sea levels exacerbate these events, increasing the risk of coastal flooding and storm surges.
Question 3: What are the implications of sea level rise for coastal communities and ecosystems?
Sea level rise threatens coastal communities and infrastructure, causing erosion, flooding, and salinization of freshwater sources. It can also lead to the loss of coastal habitats, harming marine ecosystems and the species that rely on them.
Question 4: How does ocean acidification impact marine life and ecosystems?
Ocean acidification occurs as the ocean absorbs carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, making it more acidic. This can damage the shells and skeletons of marine organisms, impair their ability to reproduce and grow, and disrupt the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
Question 5: What are the consequences of the loss of biodiversity due to climate change?
The loss of biodiversity has severe implications for the stability and resilience of ecosystems. It can disrupt food chains, reduce ecosystem services, and make it more challenging for humans to adapt to climate change, as biodiversity provides essential resources like food, medicine, and shelter.
Question 6: What can be done to mitigate the environmental effects of climate change?
Mitigating the environmental effects of climate change requires collective action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. This includes transitioning to renewable energy sources, promoting energy efficiency, protecting forests, and implementing sustainable agricultural practices. Individual choices, such as reducing consumption and adopting eco-friendly lifestyles, can also contribute to these efforts.
In conclusion, the environmental effects of climate change are far-reaching and pose significant threats to the planet and its inhabitants. Understanding these effects is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate climate change and protect the environment for future generations.
Transition to the next article section: For more in-depth information on the environmental effects of climate change and the actions we can take to address them, explore the resources provided in the following section.
Tips for Mitigating Environmental Effects of Climate Change
Climate change poses significant environmental challenges, but we can take collective action to mitigate its impacts and protect our planet.
Tip 1: Transition to Renewable Energy
Replace fossil fuel-based energy sources with renewable alternatives such as solar, wind, and geothermal. This reduces greenhouse gas emissions and promotes a clean energy future.
Tip 2: Improve Energy Efficiency
Implement energy-efficient measures in homes, buildings, and industries. This includes insulation, energy-efficient appliances, and smart energy management systems.
Tip 3: Protect Forests
Forests absorb carbon dioxide, acting as natural carbon sinks. Conserve and sustainably manage forests to maintain their carbon sequestration capacity.
Tip 4: Implement Sustainable Agriculture
Adopt agricultural practices that minimize greenhouse gas emissions, such as no-till farming, precision fertilizer application, and efficient water management.
Tip 5: Reduce Consumption
Reduce excessive consumption of goods and services. Choose durable products, repair or reuse items, and opt for sustainable alternatives.
Tip 6: Support Climate-Friendly Policies
Advocate for policies that promote renewable energy, energy efficiency, and climate change mitigation. Engage with policymakers and support organizations advocating for environmental conservation.
Tip 7: Educate and Raise Awareness
Educate others about the environmental effects of climate change and encourage them to adopt sustainable practices. Knowledge empowers individuals to make informed decisions and contribute to collective action.
By implementing these tips, we can collectively mitigate the environmental effects of climate change, protect our planet, and ensure a sustainable future for generations to come.
Conclusion
The environmental effects of climate change pose significant challenges to our planet and its inhabitants. From rising global temperatures and extreme weather events to sea level rise and ocean acidification, the impacts are far-reaching and demand our attention.
Understanding these effects is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate climate change and protect the environment for future generations. By transitioning to renewable energy, improving energy efficiency, protecting forests, implementing sustainable agricultural practices, reducing consumption, and supporting climate-friendly policies, we can collectively make a difference.
Youtube Video: